Libraries
Background
This page suggests some steps for getting started with Tollos using the Primer2 board development board.
This tutorial first checks that the Tollos sample application works on your Primer2, and then steps through the processes for connecting it to a terminal. Finally, it shows how to modify and recompile the application. Please see the sample application page for an annotated description of the code (this shows a generic sample – the port and pin choices are different for the Primer2).
It is assumed for this tutorial that you are using a computer on which the operating system is Windows (XP, Vista, or 7), as this is the more complicated option. The steps for (say) a Linux host are very similar.
It is also assumed that you have installed the software that is provided with the Primer2, although the only program from it which used in this tutorial is Cortex_pgm, to flash the Primer2’s program memory (ROM).
Check the sample application
- Download the Tollos package from the download page
(e.g., tollos115.zip).
- Unzip the package in the location of your choice, preserving its
directory structure. This should create a directory called tollos,
within which there should be at least these five directories:
psample – the sample application for Primer2
tollos – the Tollos core library
primer2 – the library for Primer2 (board-dependent code and link script)
stmf10x – the library for the STM32F103VE (the microcontroller used on the Primer2 board)
stmvcom – the library for the USB Virtual COM port.
- Inside
the psample directory there should be a file called psample.hex.
This is the compiled binary code for the sample application (in hexadecimal).
To write this to the Primer2 board:- Note this will overwrite any existing software and applications on the Primer2, such as CircleOS; see the Primer2 user manual for restoring the factory configuration.
- Attach the Primer2 to your computer with the USB cable to the DEBUG port.
- If the Primer2 display is not lit, press the Primer2 joystick button.
- Open a command window prompt (usually in the Accessories folder in Start programs) and change directory to the tollos\psample directory (use the CD command).
- Type in and enter the command:
flash
This should result in a number of lines being displayed, ending with
(3)
Closing com with RLink... OK
At this point the red user LED (near the centre, at the opposite end to the USB sockets) will blink once and then the green user LED should begin blinking (on and off once a second). If you missed the initial red blink, you can reset the Primer2 without re-flashing it using the res command which is also in the psample directory.
If the LEDs do not blink, try following the above steps again, and also see the Primer2 user manual. In particular, if Windows reports that ‘Cortex_pgm’ is not recognized as an internal or external command... then check that the Primer2 software is installed and that its bin directory (probably c:\Program Files\Raisonance\Ride\bin) is included in your PATH environment variable.
Using a terminal with Primer2
The sample application uses the Tollos debug functions to communicate with a terminal emulator on the PC: the debugf function (a small version of the C function printf) is used to write character strings to the terminal, and the debugGetc function lets it receive characters that you type on the terminal. These both use the Tollos Virtual COM port functions, which emulates a serial COM port over a USB connection to the board.For this to work, you need:
- terminal emulator software for the PC
- (on Windows) the USB serial port driver for the STM USB device (this should be found automatically by Windows).
In brief, the steps are:
- Install a terminal emulator. TeraTerm is recommended because it
is easier to use than most;
Putty is one
of several other possibilities.
- Download the TeraTerm installer file (e.g., teraterm-4.67.exe).
- Run the installer to install TeraTerm (you can skip the LogMeTT and TTLEditor installs).
- Connect the Primer2 USB port (the one marked “STM32”) to the host
PC. Note that you can leave the “DEBUG” USB port connected, for
downloading a changed application (see below). This will need two
USB cables.
- Windows should now either automatically start installing a driver (Windows 7) or will start the driver installlation Wizard (Windows XP). If the latter, follow the instructions and allow Windows to search for the driver. This may take some minutes.
- If the driver is not found, try manually installing it by clicking on stmvirtcom.inf which is in the stmvcom\public directory.
- Start the TeraTerm emulator
- choose File → New Connection (this window may pop up automatically) and then select ‘Serial’
- available ports will then be listed; select the Primer2 (STM) port, which should be listed by name
- then click OK.
- Next choose Setup → Serial port
- against ‘Baud rate:’ select 115200
- then click OK.
- (You might want to save these settings so they will be used next time: choose Setup → Save Setup...)
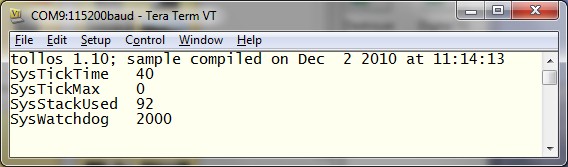
At this point the terminal is ready to use; a short message (queued up from when the Primer2 was last reset) should appear on the terminal (similar to the first content line in the image below). If you see nothing at all then check the steps above, and also try reseting the Primer2 using the res command in the psample directory.
Assuming the terminal is working, the sample application will be watching out for certain characters which you can type in. These include:
- 1 – invert the state of LED1 (red, on ↔ off)
- 0 – similarly inverts LED0 (green)
- ? – prints some system information values to the terminal.
Here’s how the TeraTerm window might look after a reset and the character ? being typed:
Note that the terminal application should be started after resetting the Primer2 and stopped before any further reset or download. If you forget to do this, no new output will show: in this case, stop the terminal and reset the Primer2 again before starting it.
Also, after powering of the Primer2 you may need to press the joystick button to restart it, as described earlier.
Modify the application
To modify the sample application you need- A text editor (such as Windows Notepad)
- A cross compiler (a compiler that runs on a PC and lets you compile programs for the ARM processor on the mbed board).
Tollos is compiled with the free CodeSourcery G++ Lite cross compiler for ARM EABI, and this tutorial assumes you are using that, although there are other options (in particular, the Primer2 software includes a different version of the same compiler, which can probably be used – you might prefer to try this first). If you are using a different compiler you may need to recompile all the Tollos libraries (using the churn command in each library) as well as the sample application.
The steps are:
- Download and install CodeSourcery G++ Lite (for most Windows installations, use the EABI
download suggested and select the IA32 Windows Installer).
Accepting all the defaults (including setting the PATH) is recommended (at the sixth step you might also want icons to be added to the start menu, etc., but that is not essential). - Make a change to the sample application (psample.c in the subdirectory
psample in your tollos directory) with your text editor (see
the annotated version for a description of the
application), perhaps:
– change the LED that is blinked in the init() function to LED0 and increase the sysPause time while it is on
– turn off the display backlight by adding to the init() function the line
bitSet(PORTB, BIT8, BIT_OFF);
then save the file. - Open a command window prompt and change directory to the tollos\psample
directory.
- Type in and enter the command:
churn
This should result in the following lines being displayed:
psample.c Compiled OK
Linked OK
psample.hex created OK, size 10115 bytes
Press any key to continue . . .
(the size might be different than shown here).If this fails, you should see some error message that describes the problem (for example, if the compiler cannot be found it is likely that the PATH was not set during installation). See also the FAQ page.
- At this point, the sample application has been compiled and a new
binary file (psample.hex) has been created:
– press any key (to complete the churn command)
– flash the binary to the Primer2 using the flash command (see above)
– use the res command as required to watch the program restart (remember to stop the terminal first and then restart it afterwards, if you are using a terminal).
You can now continue to modify the sample, or you can write your own. The churn command can be used to compile different programs by specifying the name of the .c file (including the .c) as the first parameter word. You can also use it from Windows Explorer by dragging the application .c file and dropping it onto the churn icon; in this case a window will be opened automatically to display the compilation results etc.
The churn command is a plain-text file (churn.bat) which includes the names of the libraries, etc., that are used to build the application – you can view or edit this with Notepad. Other examples of code and churn.bat scripts can be found in the other Tollos directories.
All of the steps above have been tested, but software configurations can vary. If you come across any errors in this page, or suggestions for improvements, please let me know.